Hello! I am a Ph.D student at HIT, advised by Junbao Li and Huanyu Liu.
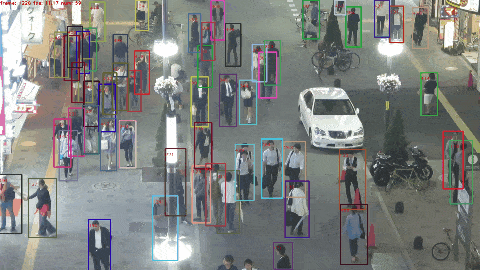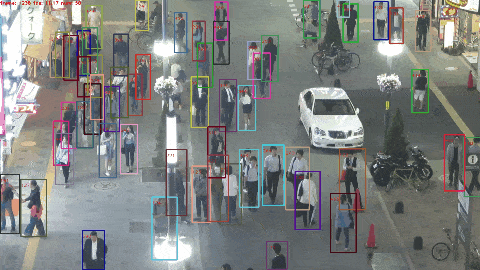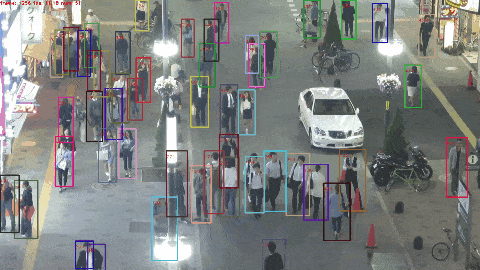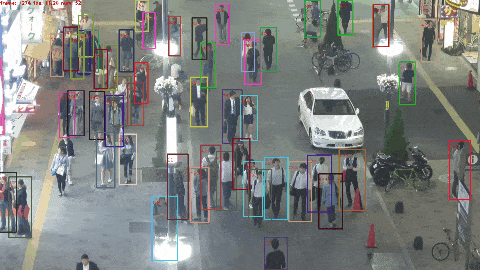
My name is Jiazheng Wen and english name is Joshua Wen. In 2017, I received a bachelor's degree in information engineering from Xi'an Jiaotong University. In 2022, I received a master's degree in electronic science and technology from Harbin Engineering University. Nowadays, I am studying for a Ph.D in Faculty of Computing, Harbin Institute of Technology. I worked as a research intern at Focused Loong Technology Co.,Ltd. from 2019-2022. My research focuses on deep reinforcement learning and vision enhancement.
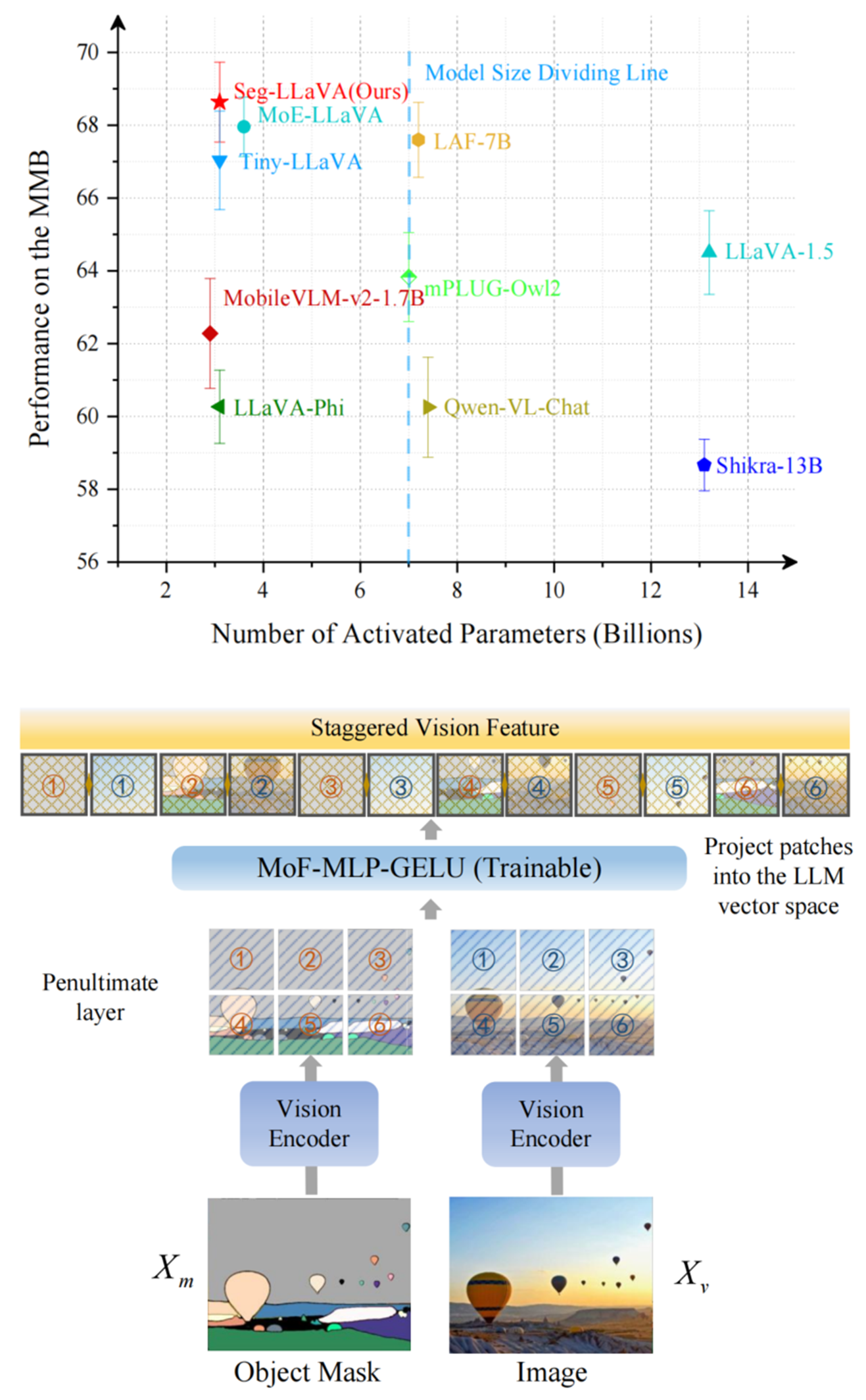
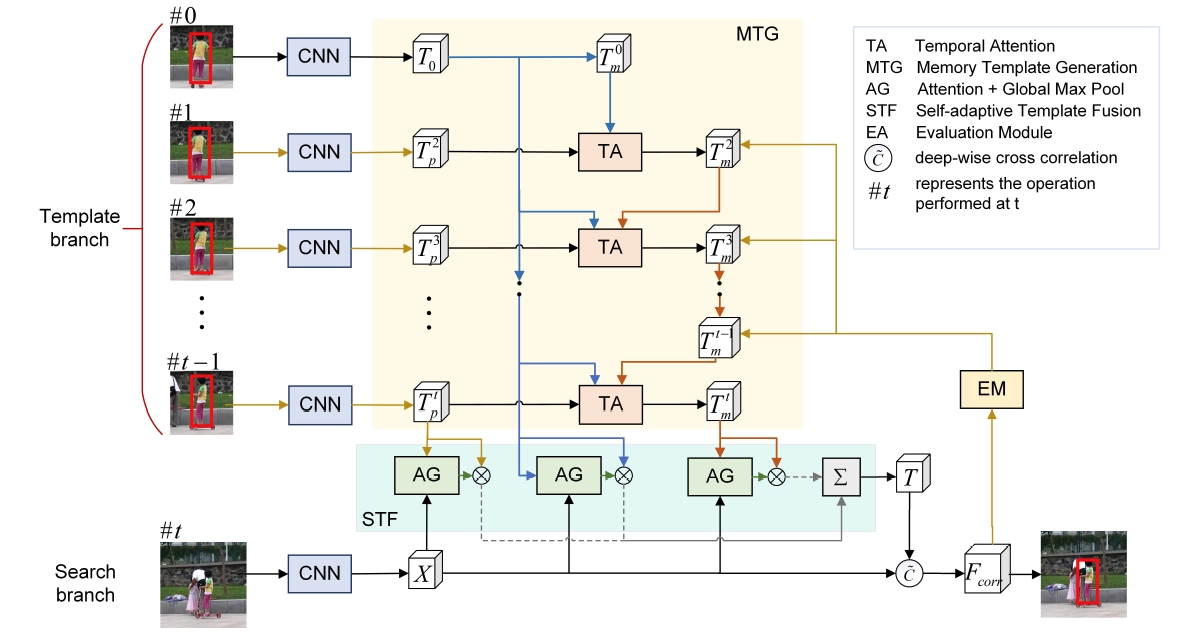
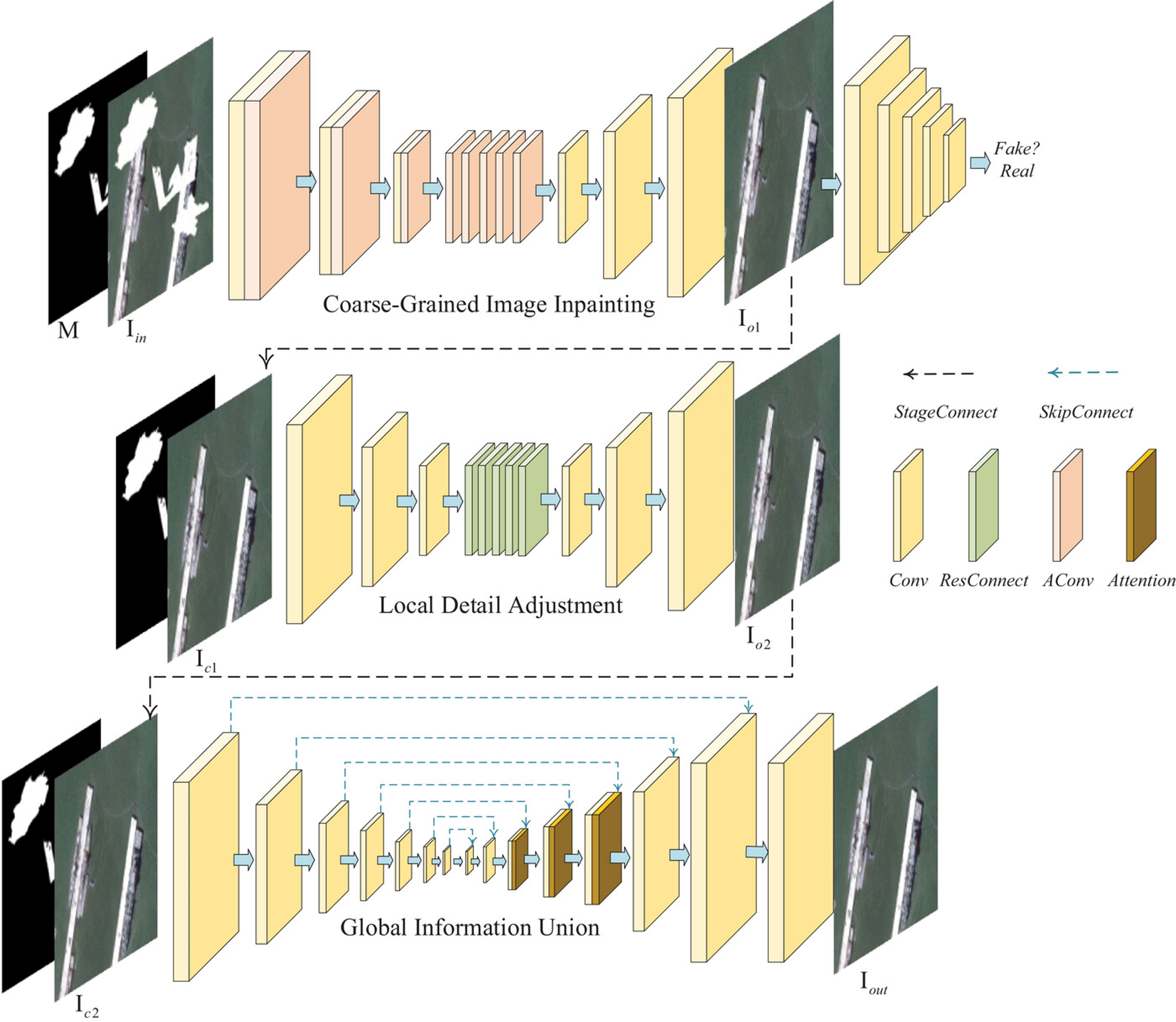
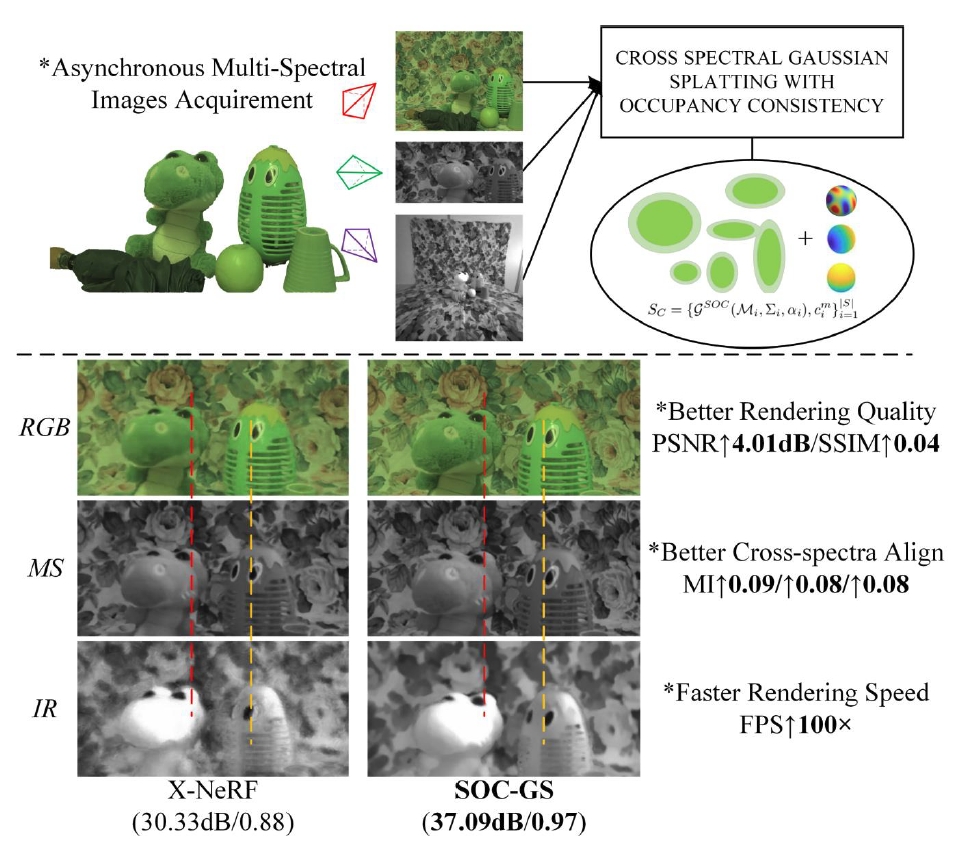
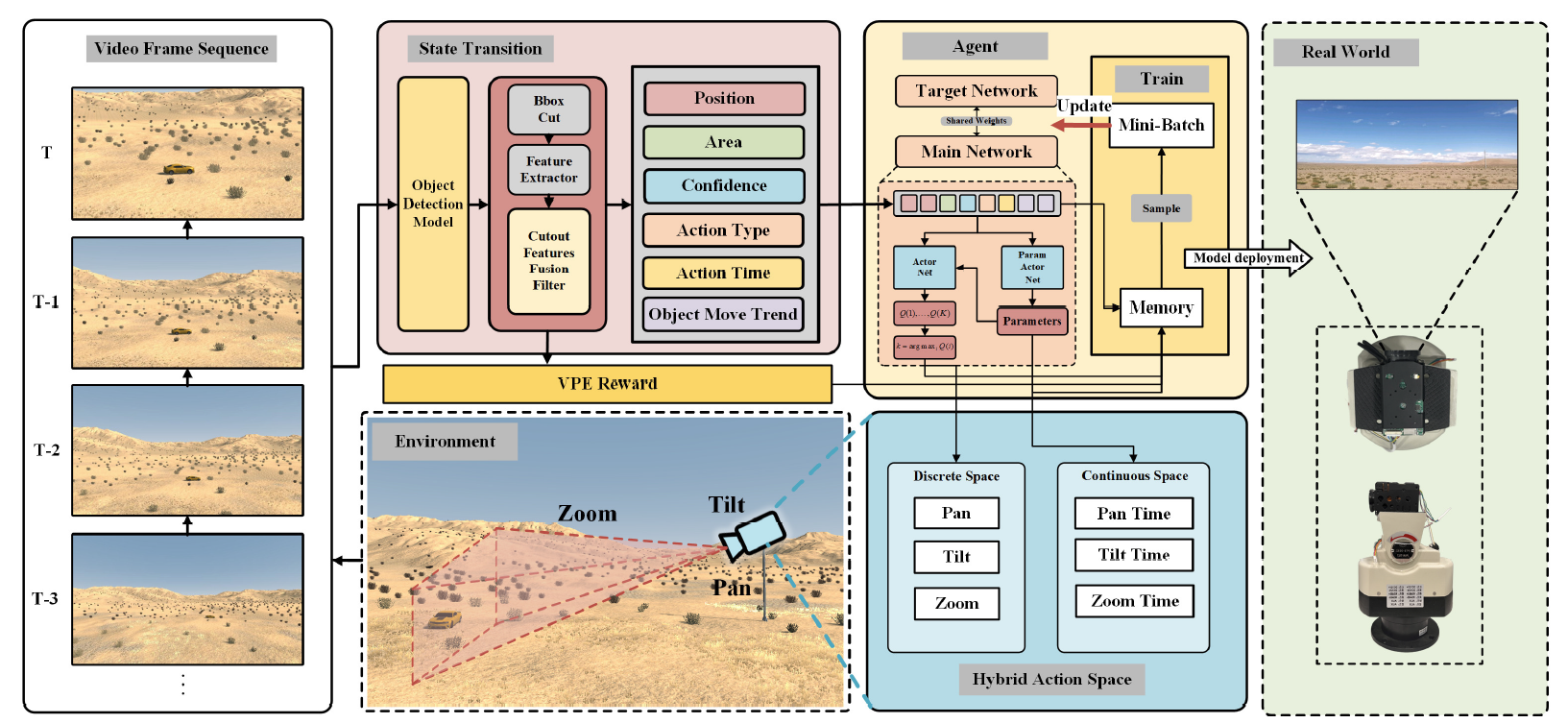
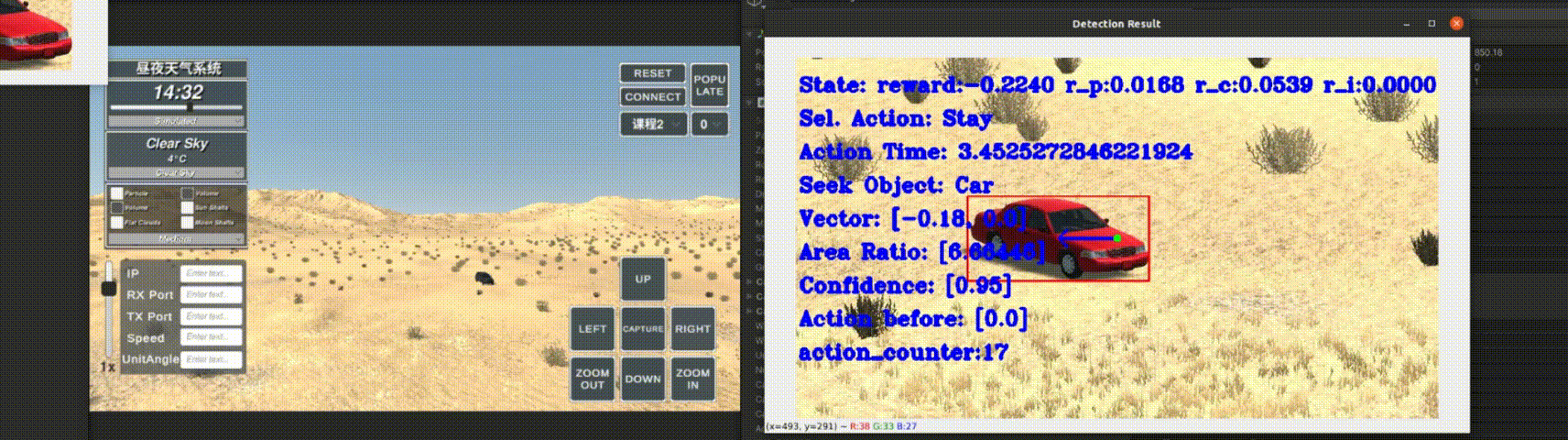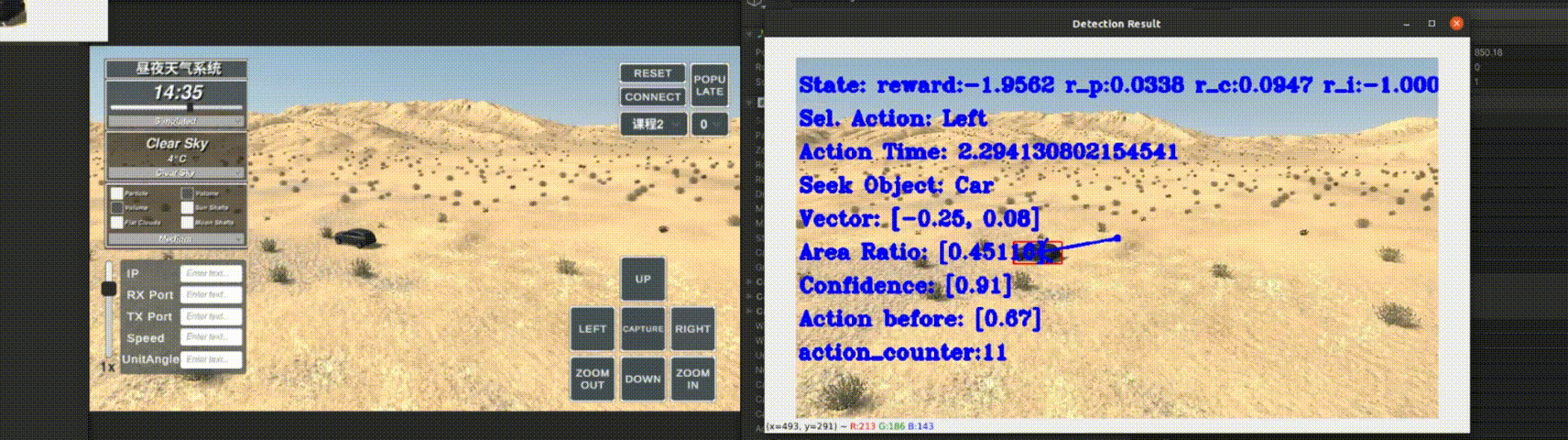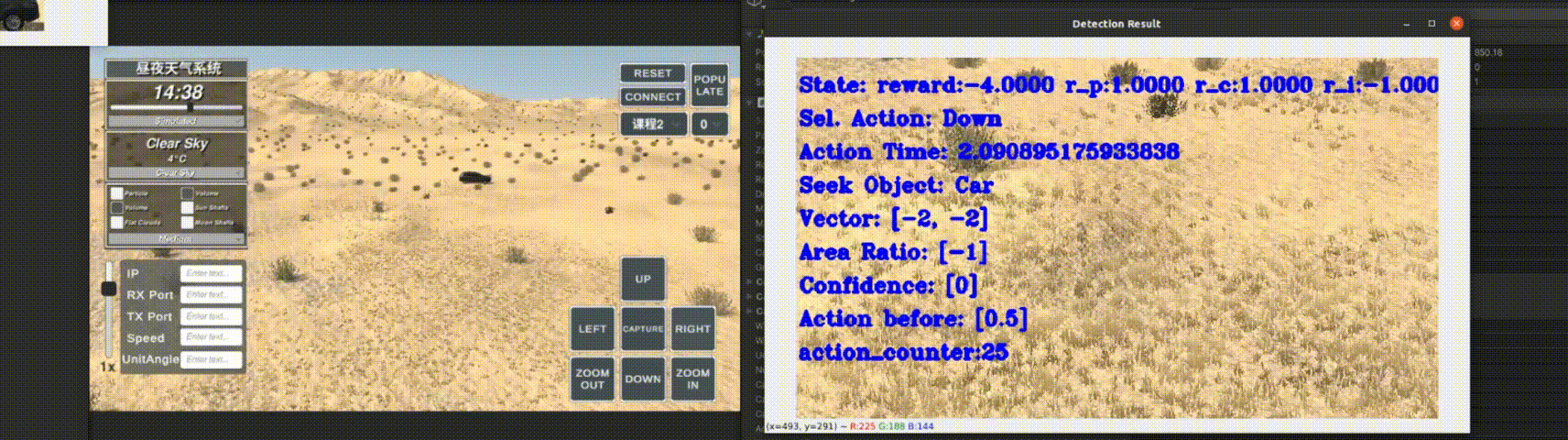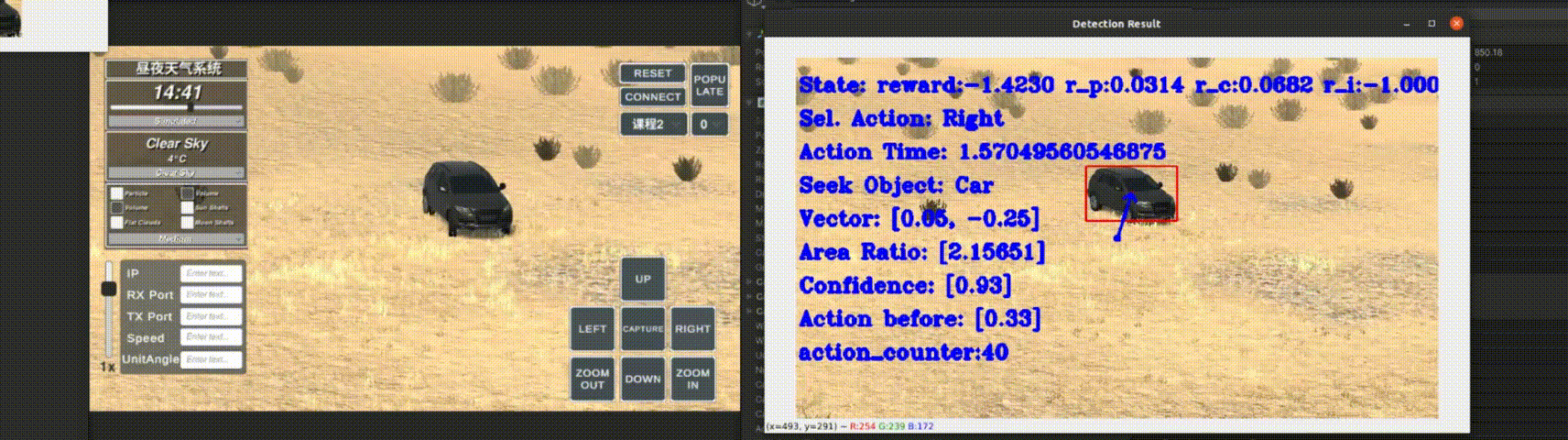
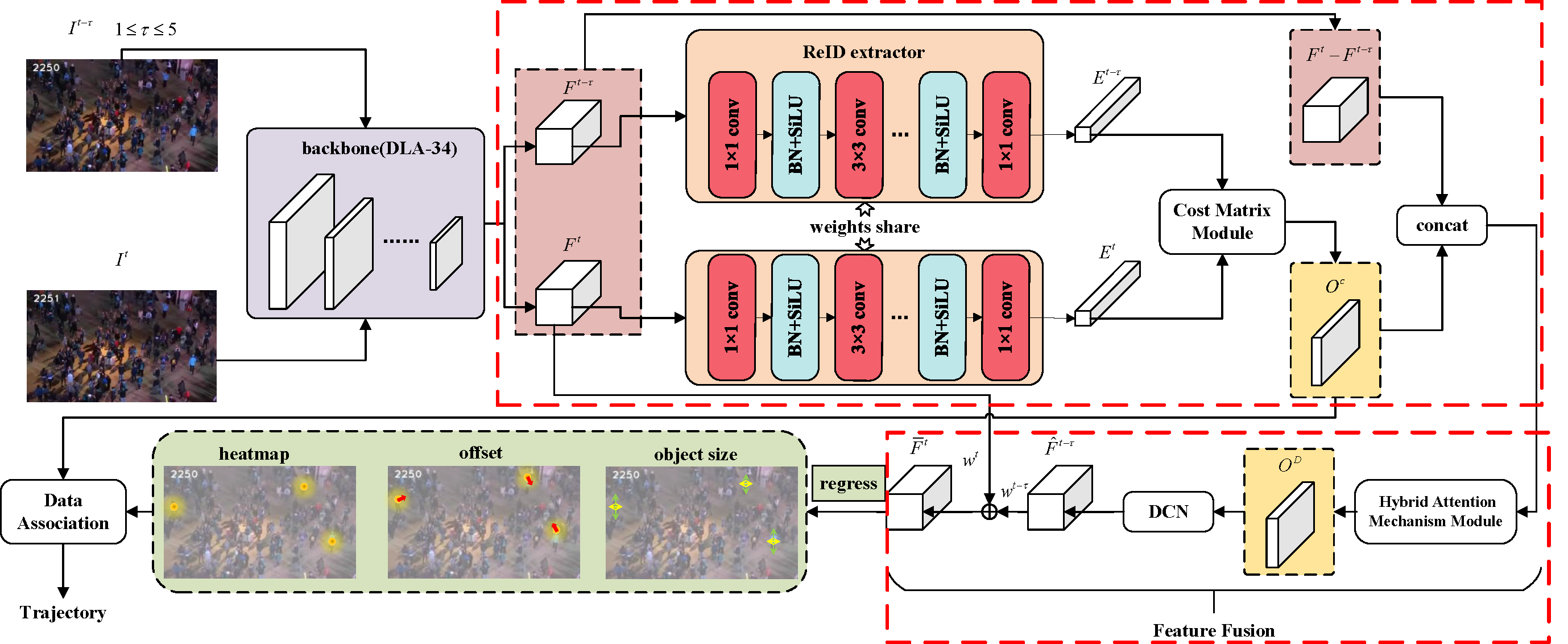
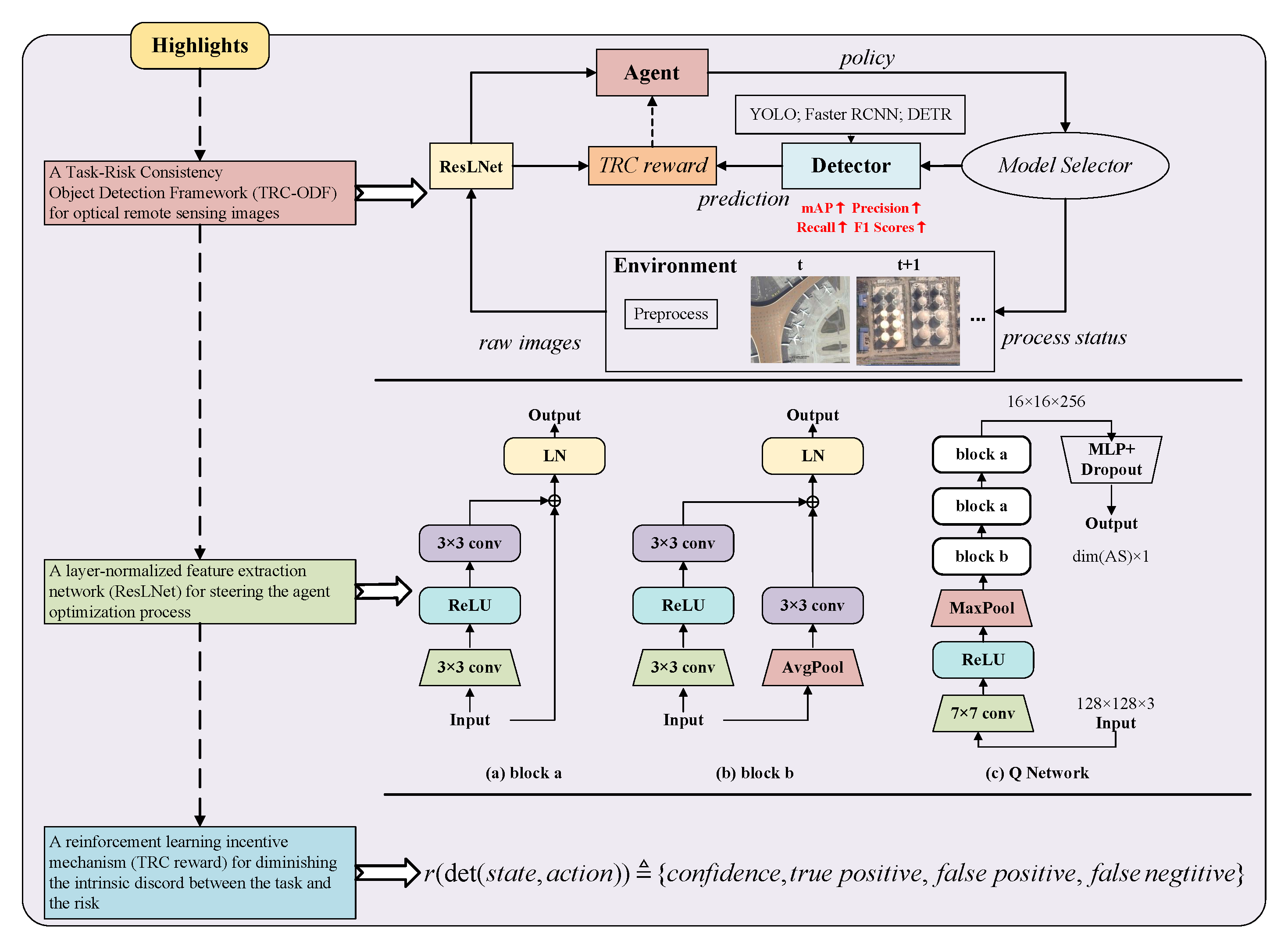
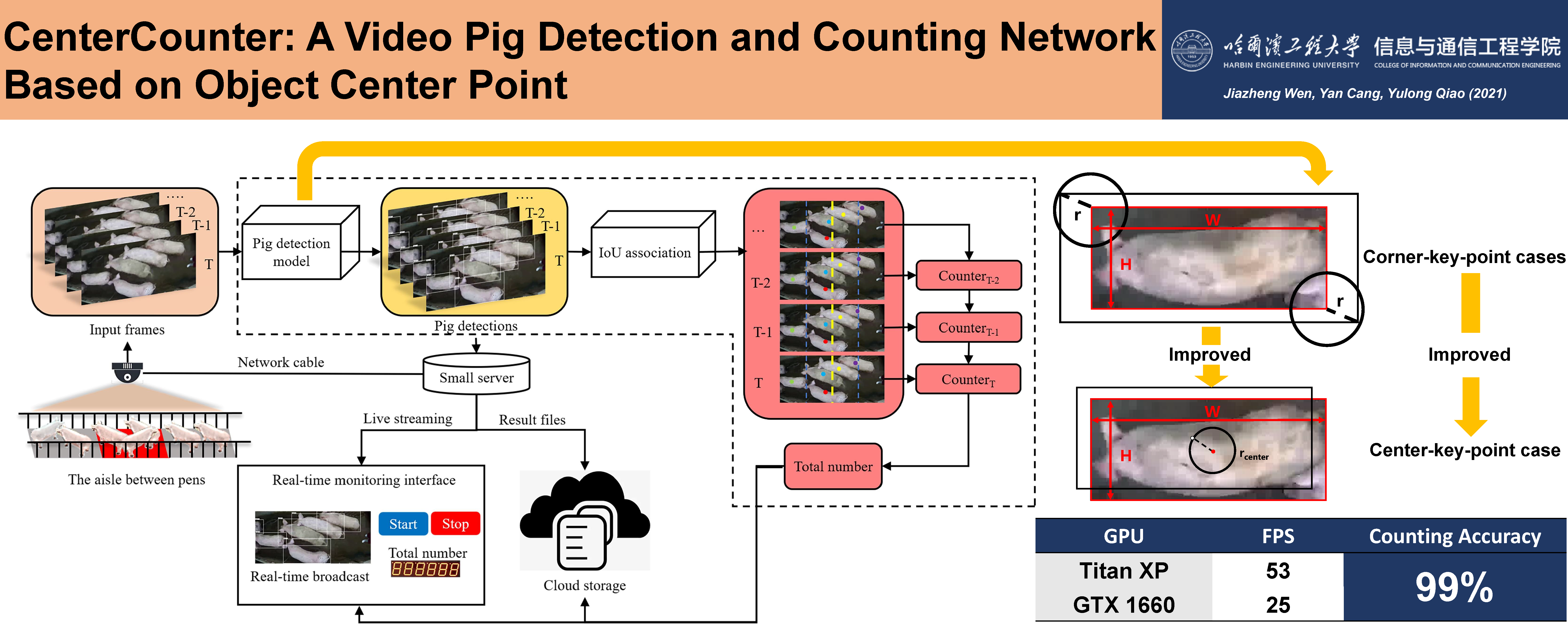
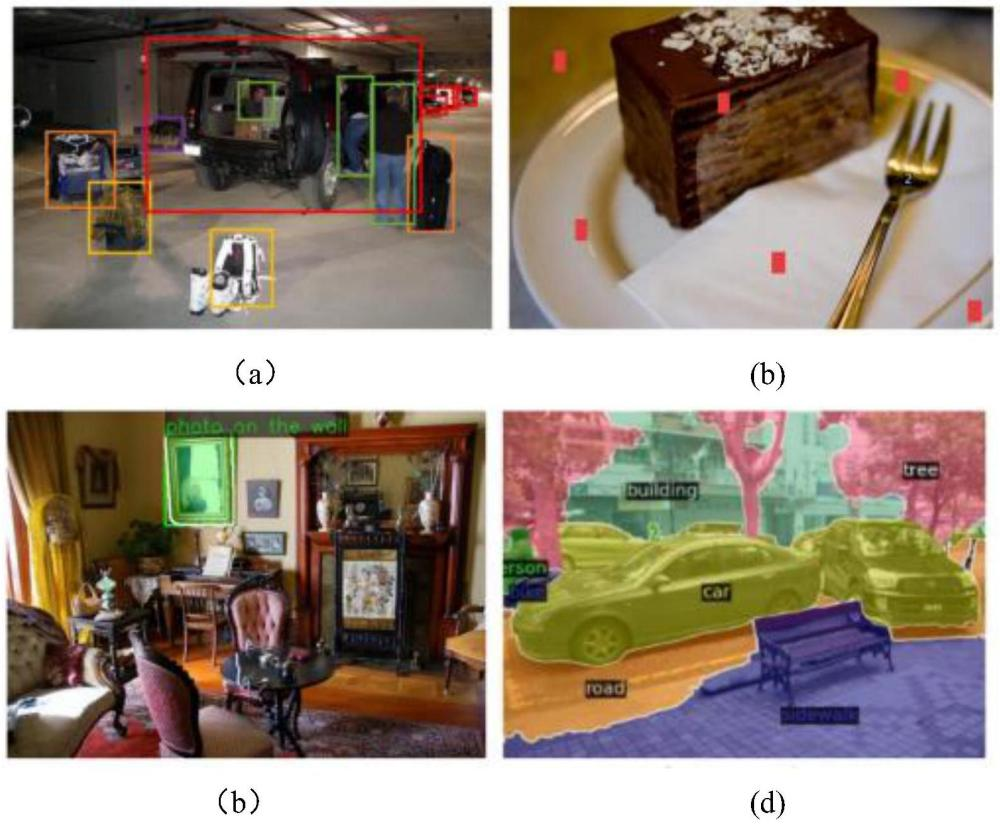
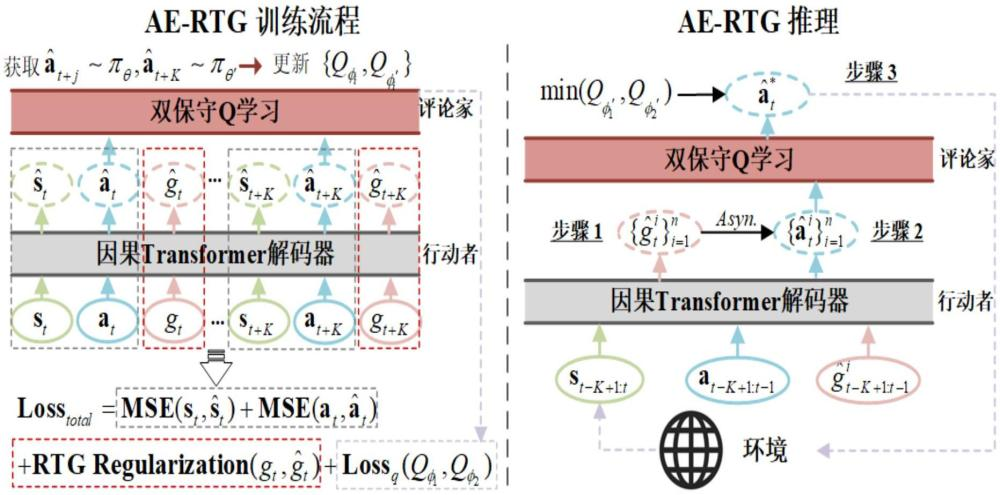
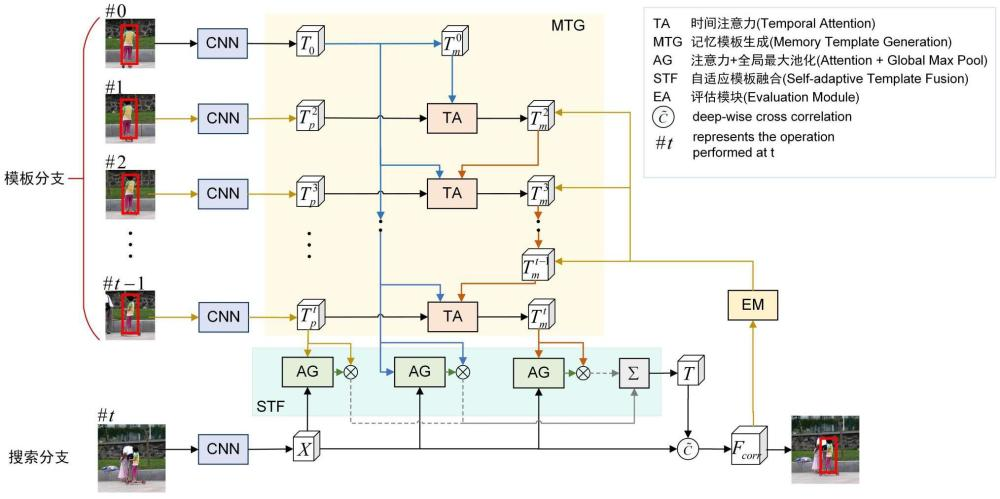
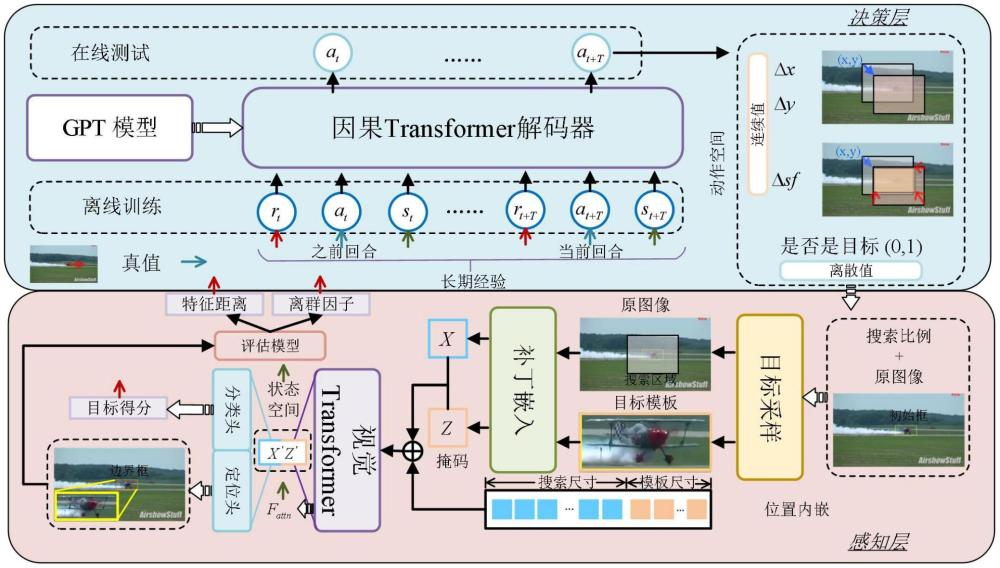
Currently, my main interest is in how to enhance the perception of computer vision algorithms through deep reinforcement learning. If you want to discuss anything research related, please feel free to reach me :)
Email / ORCID / Google Scholar / Github / GitHub Stars: 63